Booting a computer in safe mode is a troubleshooting option that starts the operating system with a minimal set of drivers and services. This can help identify and fix problems with the system, especially when dealing with issues caused by third-party software or drivers. The process of entering safe mode can vary slightly depending on the operating system. I'll provide instructions for Windows, macOS, and Linux.
Safe Mode in Windows:
Windows 10/8:
- Press the Windows key + I to open Settings.
- Select "Update & Security."
- Choose "Recovery" from the left sidebar.
- Under the "Advanced startup" section, click "Restart now."
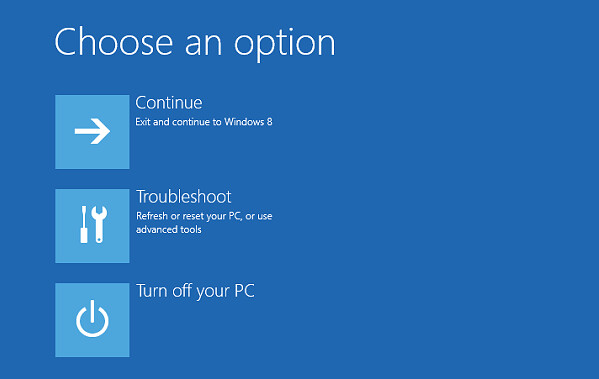
- After the restart, select "Troubleshoot" > "Advanced options" > "Startup Settings" > "Restart."
- Press the 4 or F4 key to start in Safe Mode, or press 5 or F5 for Safe Mode with Networking.
Alternatively, you can press the F8 key repeatedly during the computer's boot process before the Windows logo appears. However, this method might not work on newer systems.
Windows 7 and earlier:
- Restart your computer.
- Press the F8 key repeatedly before the Windows logo appears.
- Use the arrow keys to select "Safe Mode" and press Enter.
Safe Mode in macOS:
Mac with Intel processor:
- Shut down your Mac.
- Turn it on and immediately hold down the Shift key.
- Release the Shift key when you see the Apple logo or login window.
Mac with Apple Silicon (M1) processor:
- Shut down your Mac.
- Turn it on and hold down the power button until you see "Loading options."
- Select your startup disk, and then press and hold the Shift key while clicking "Continue in Safe Mode."
Safe Mode in Linux (Ubuntu example):
Grub Menu:
- Restart your computer.
- When the Grub menu appears (usually after the BIOS/UEFI screen), use the arrow keys to select the Linux kernel you want to boot.
- Press the "e" key to edit the boot parameters.
- Find the line starting with "linux" and add "single" or "3" (without quotes) at the end.
- Press Ctrl + X to boot with the modified settings.
Keep in mind that accessing safe mode might vary based on your system's manufacturer and specific configuration. Always refer to your system documentation if you encounter any issues or if these steps don't work for your particular setup.







No comments:
Post a Comment